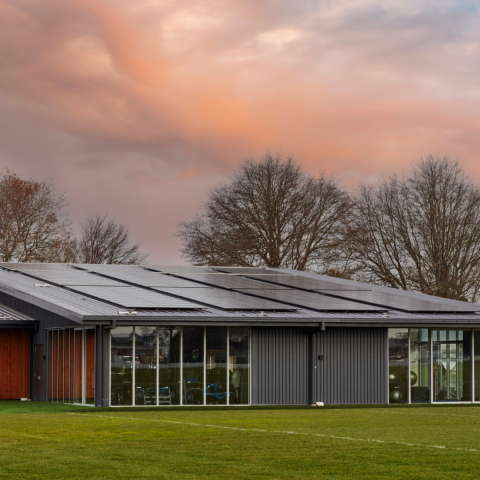
Electricity can be generated from the sun in a number of ways, but in most New Zealand residential solar power applications it’s photovoltaic solar panels that use sunlight to produce power. This type of solar energy is often abbreviated to PVs.
Heat-based solar power, referred to as concentrated solar thermal or concentrated solar power, is another common type of energy generated from the sun. It’s popular in large plant-scale and water-heating operations.
In a PV-based solar power solution:
- Photons of light from the sun hit installed solar panels with semiconductive cells mounted to them.
- The photons excite electrons around the atoms in these cells, leading to a ‘charge’.
- A solar power system then converts the Direct Current (DC) electricity into Alternating Current (AC) electricity – the power that’s appropriate to power our wall plugs, appliances and lighting.
- The transition from DC to useable AC is managed through a solar inverter.
- Some systems have battery components, enabling power to be stored for later use.